Does MMD Really Align? A Cross Domain Wireless Sensing Method via Local Distribution
Abstract
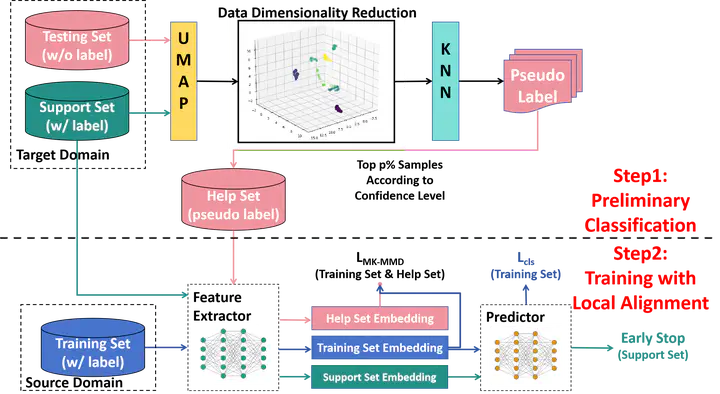
In wireless sensing, Channel State Information (CSI) is commonly used for detecting human behavior, but its sensitivity to environmental changes can degrade performance when models trained in one environment are applied to another. To tackle this, Domain Alignment (DAL), particularly the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD), is often employed to align the global distributions of source and target domains. However, DAL typically overlooks inter-category relationships, leading to misalignment even with global alignment. To address these limitations, we propose K-Nearest Neighbors Maximum Mean Discrepancy (KNN-MMD), a novel few-shot method for cross-domain wireless sensing. Our approach constructs a ``help set" using K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) from the target domain, enabling local alignment within each category via MMD. We also address the instability often seen in cross-domain methods, where performance fluctuates between epochs, and the challenge of determining an optimal stopping point during training due to the lack of labeled data. Our method resolves this by excluding the support set from the target domain during training and uses it as a validation set for early stopping. We evaluate the effectiveness of KNN-MMD on cross-domain Wi-Fi gesture recognition and people identification tasks, achieving accuracy rates of 93.26% and 81.84% in one-shot scenarios. The dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/RS2002/KNN-MMD.